[Avg. reading time: 14 minutes]
Important Concepts
Date format
Epoch Time: Unix Time is the number of seconds that have elapsed since Jan 1 1970 UTC.
https://www.epochconverter.com/
It uses 32 Bit Integer, so by Jan 19, Y2038 we will run out of storage and companies gradually upgrading it as they upgrade their systems.
-
Binary : 0 - 1
-
Octal : 0 - 7
-
Hex : 0 - 9, A - F
-
Base 10 a.k.a Decimal Numbers : 0 - 9
-
Base 36 : 0 - 9 + A - Z
Base 36 is the most compact case-insensitive alphanumeric numbering system.
Popular Use Cases:
- Base 36 is used for Dell Express Service Codes, website url shorteners and many other applications which have a need to minimize human error.
- Reduce cloud storage cost.
https://www.rapidtables.com/convert/number/base-converter.html
Example: Processing 1 billion rows each hour for a day
Billion rows x 14 = 14 billion bytes = 14 GB x 24 hrs = 336 GB
Billion rows x 8 = 8 billion bytes = 8 GB x 24 hrs = 192 GB
Base 64:
Base64 encoding schemes are commonly used when there is a need to encode binary data that needs be stored and transferred over media that are designed to deal with textual data. This is to ensure that the data remains intact without modification during transport.
Base64 is a way to encode binary data into an ASCII character set known to pretty much every computer system, in order to transmit the data without loss or modification of the contents itself.
2 power 6 = 64
So Base64 Binary values are six bits not 8 bits.
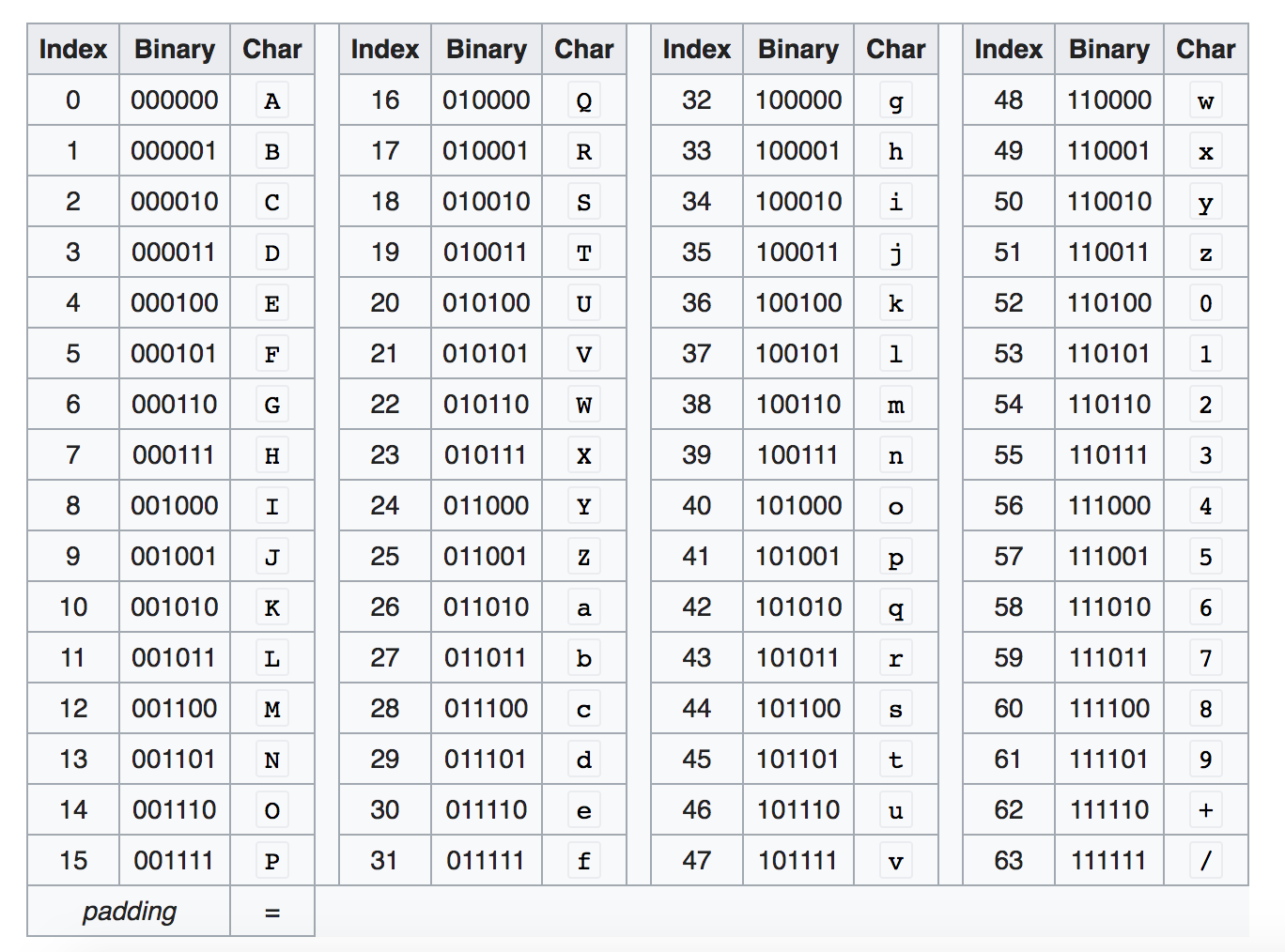
Base64 encoding converts every three bytes of data (three bytes is 3*8=24 bits) into four base64 characters.
Example:
Convert Hi! to Base64
Character - Ascii - Binary
H= 72 = 01001000
i = 105 = 01101001
! = 33 = 00100001
Hi! = 01001000 01101001 00100001
Split into 4 parts
010010 000110 100100 100001
S G k h
How about converting Hi to Base64
010010 000110 1001
Add zeros in the end so its 6 characters long
010010 000110 100100
Base 64 is SGk=
= is the padding character so the result is always multiple of 4.
Another Example
convert f to Base64
102 = 01100110
011001 100000
Zg==
Think about sending Image (binary) as JSON, binary wont work. But sending as Base64 works the best.
https://elmah.io/tools/base64-image-encoder/
Demo Img HTML
base64 = "0.22.1"
// Convert to Base64
use base64::encode;
fn main() {
let string = "Hello world!";
let encoded = encode(string);
println!("Base64: {}", encoded);
let bin_string = b"Hello world!";
let encoded1 = encode(bin_string);
println!("Base64: {}", encoded1);
}
Convert Base64 to String
// Convert to String
use base64::{encode,decode};
use std::str;
fn main() {
let string = "Hello world!";
let encoded = encode(string);
println!("Base64: {}", encoded);
let decoded = decode("SGVsbG8gd29ybGQh").unwrap();
println!("{:?}",decoded);
let converted_string = str::from_utf8(&decoded).unwrap();
println!("{:?}",converted_string);
}
Image to Base64
cargo add base64
Store a image named sample.jpg at the same level as src (not inside src)
use std::fs::File;
use std::io::{self, Read, Write};
use base64::{engine::general_purpose, Engine as _};
fn main() -> io::Result<()> {
// Read the image file
let mut image_file = File::open("sample.jpg")?;
let mut image_data = Vec::new();
image_file.read_to_end(&mut image_data)?;
// Encode the image data to Base64
let base64_encoded = general_purpose::STANDARD.encode(&image_data);
// Write the Base64 encoded string to a new file
let mut output_file = File::create("output_base641.txt")?;
output_file.write_all(base64_encoded.as_bytes())?;
println!("Base64 encoded image data has been written to output_base64.txt");
Ok(())
}
Read from Base64 to Image
use std::fs::File;
use std::io::{self, Read, Write};
use base64::{engine::general_purpose, Engine as _};
fn main() -> io::Result<()> {
// Read the Base64 encoded text file
let mut base64_file = File::open("output_base64.txt")?;
let mut base64_string = String::new();
base64_file.read_to_string(&mut base64_string)?;
// Decode the Base64 string to binary image data
let image_data = general_purpose::STANDARD.decode(&base64_string).expect("Failed to decode Base64 string");
// Write the binary image data to a new image file
let mut output_image_file = File::create("decoded_image.jpg")?;
output_image_file.write_all(&image_data)?;
println!("Image has been decoded and written to decoded_image.jpg");
Ok(())
}
````<span id='footer-class'>Ver 2.0.15</span>
<footer id="last-change">Last change: 2026-02-25</footer>````