[Avg. reading time: 16 minutes]
Big O Notation
Algorithmic Complexity
When analyzing an algorithm,
Time Complexity: The time it takes to execute the code. Space Complexity: The space taken in the memory to execute the code.
Following Notations are used to represent Algorithmic Complexity. Big O is what everybody is interested in.
Big - Omega = Best Case Big - Theta = Average Case BIG O = Worst Case

Will try to use general algorithms not any specific programming syntaxes.
Constant or Static Complexity - O(1)
// Defining a constant const FAHRENHEIT_CONSTANT: f64 = 32.0; // Defining a static variable static MULTIPLIER: f64 = 1.8; fn main() { println!("Enter Name:"); // Example temperature conversion calculations let fahrenheit: f64 = 100.0; // Example input let celsius = fahrenheit_to_celsius(fahrenheit); let fahrenheit_converted_back = celsius_to_fahrenheit(celsius); println!("Celsius: {:.2}, Fahrenheit: {:.2}", celsius, fahrenheit_converted_back); } fn fahrenheit_to_celsius(f: f64) -> f64 { (f - FAHRENHEIT_CONSTANT) / MULTIPLIER } fn celsius_to_fahrenheit(c: f64) -> f64 { (c * MULTIPLIER) + FAHRENHEIT_CONSTANT }
Each line is of complexity O(1). Because its handling only one item.
n * O(1);
n is the number of lines.
While finding the pattern we ignore the constant values.
So we remove n and the complexity is O(1)
Linear Complexity O(N)
In this case the time and size changes based on number of input values.
For example
// Linear Complexity
for i = 1 to N
print (i)
if N = 10 it will be print faster, if N = 1Million the time taken will be linear.
These kinds of Linear changes is called O(N)
fn main() { // Create an array of integers let numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]; // Call the function to print the elements print_elements(&numbers); } fn print_elements(numbers: &[i32]) { // Iterate over the elements of the array for number in numbers.iter() { println!("{}", number); } }
Quadratic Complexity
// Quadratic Complexity
for i = 1 to N
for j = 1 to M
print (i,j)
fn main() { let n = 5; // Example value for N let m = 5; // Example value for M print_pairs(n, m); } fn print_pairs(n: usize, m: usize) { for i in 1..=n { for j in 1..=m { println!("({}, {})", i, j); } } }
For every i, there is another loop called j
N * N = O(N Square)
If N = 2 then the process will iterate 4 times.
What is the Complexity of these ?
for i = 1 to n
print (i)
for j = 1 to n
print (j)
for (i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < N; j++) {
sequence of statements
}
}
for (k = 0; k < N; k++) {
sequence of statements
}
for i = 1 to N
for j = 1 to M
for k = 1 to 1000
print (i,j,k)
Exponential Complexity
O(2 power N)
With the increase in input there is an exponential growth in Time and Space.
Fibonacci Series
0 1 1 2 3 5 8 13 21 34 55 89 144 233 377 610
Algorithm
function fibonacci(n){
if n = 0
return 0
if n = 1
return 1
else
return fibonacci(n - 2) + fibonacci(n - 1)
fn fibonacci(n: u32) -> u32 { if n == 0 { return 0; } if n == 1 { return 1; } return fibonacci(n - 2) + fibonacci(n - 1); } fn main() { let n = 6; println!("Fibonacci series up to {}:", n); for i in 0..=n { println!("Fibonacci({}) = {}", i, fibonacci(i)); } }
For example
(2 power n-1)
For input = 3, number of iterations is 4
graph TD
A[Fibonacci 3] --> B[Fibonacci 1]
A --> C[Fibonacci 2]
C --> D[Fibonacci 0]
C --> E[Fibonacci 1]
For input = 4, number of iterations is 8;
graph TD
A[Fibonacci 4] --> B[Finonacci 3]
A --> C[Fibonacci 2]
B --> D[Fibonacci 2]
B --> E[Fibonacci 1]
D --> F[Fibonacci 1]
D --> G[Fibonacci 0]
C --> H[Fibonacci 1]
C --> I[Fibonacci 0]
Logarithmic Complexity O(Log N)
Increase in number of input is exponential but time and space growth is Linear.
for (i= 1; i< n; i = i **2)
print(i)
or Binary Search
1 23 45 56 89 90 110 130
Pick mid point, search either left or right.
fn binary_search(arr: &[i32], target: i32) -> Option<usize> { let mut low = 0; let mut high = arr.len() - 1; while low <= high { let mid = low + (high - low) / 2; if arr[mid] == target { return Some(mid); } else if arr[mid] < target { low = mid + 1; } else { high = mid - 1; } } None } fn main() { let arr = [1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13, 15, 17, 19, 20, 21, 24, 25, 30, 44,55,56]; let target = 17; match binary_search(&arr, target) { Some(index) => println!("Target {} found at index: {}", target, index), None => println!("Target {} not found in the array", target), } }
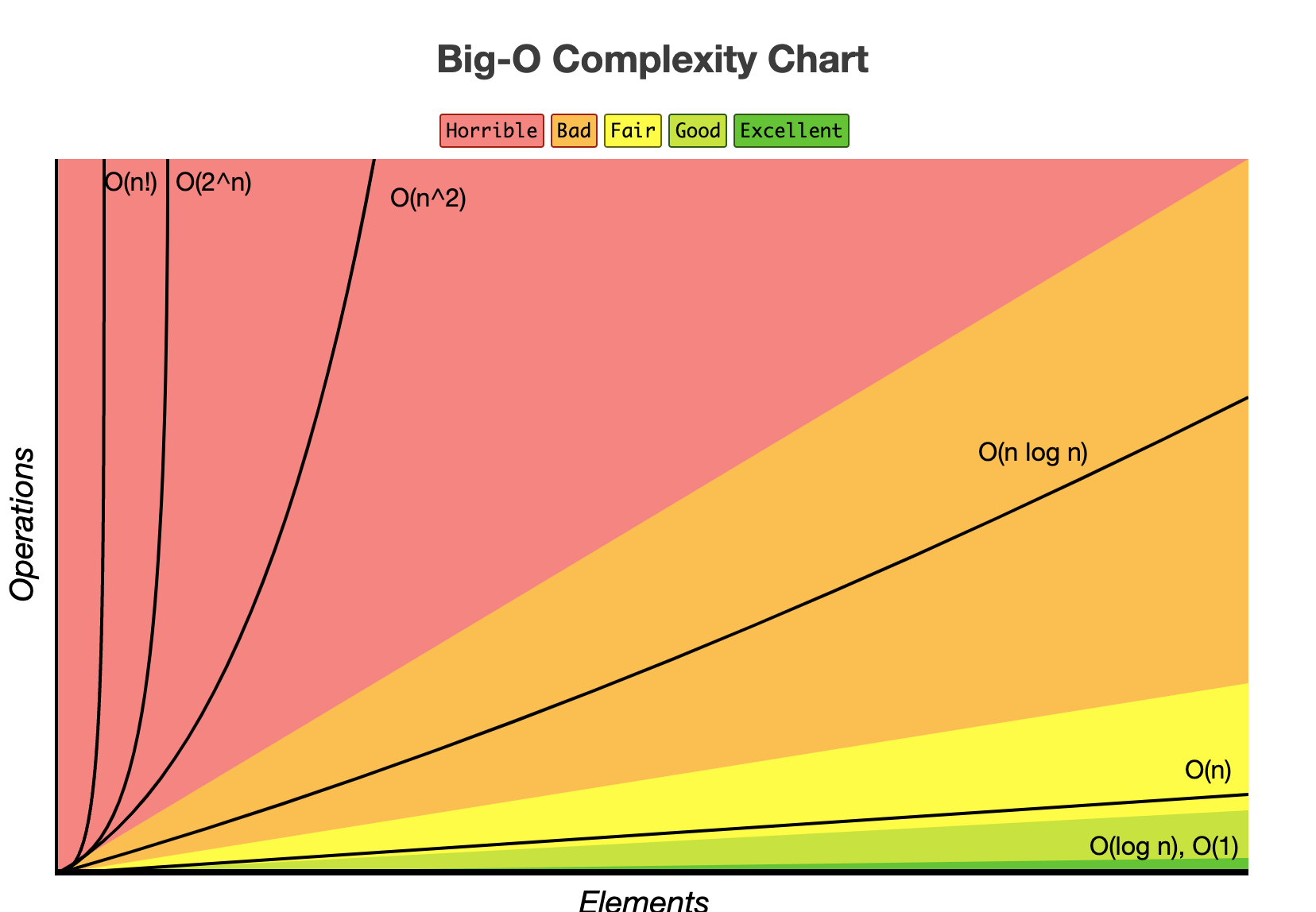
bigocheatsheet.com
Fore more visit
https://bigocheatsheet.com
Answers
- O(1)
- O(N sq)
- O(N x M)